Research
RNA splicing in mammalian brain development and disease
Coming soon…
Software development for systematic identification of differential RNA splicing
Alternative pre-mRNA splicing (AS) is a fundamental regulatory process that generates transcript diversity and cell type variation. Several computational tools have been developed to analyze AS from RNA-seq data, but they are often limited by the high false-positive rate and low reproducibility. I have developed a versatile computational method, called Shiba, that enables systematic identification of differential RNA splicing across platforms, bulk and single-cell RNA-seq data.
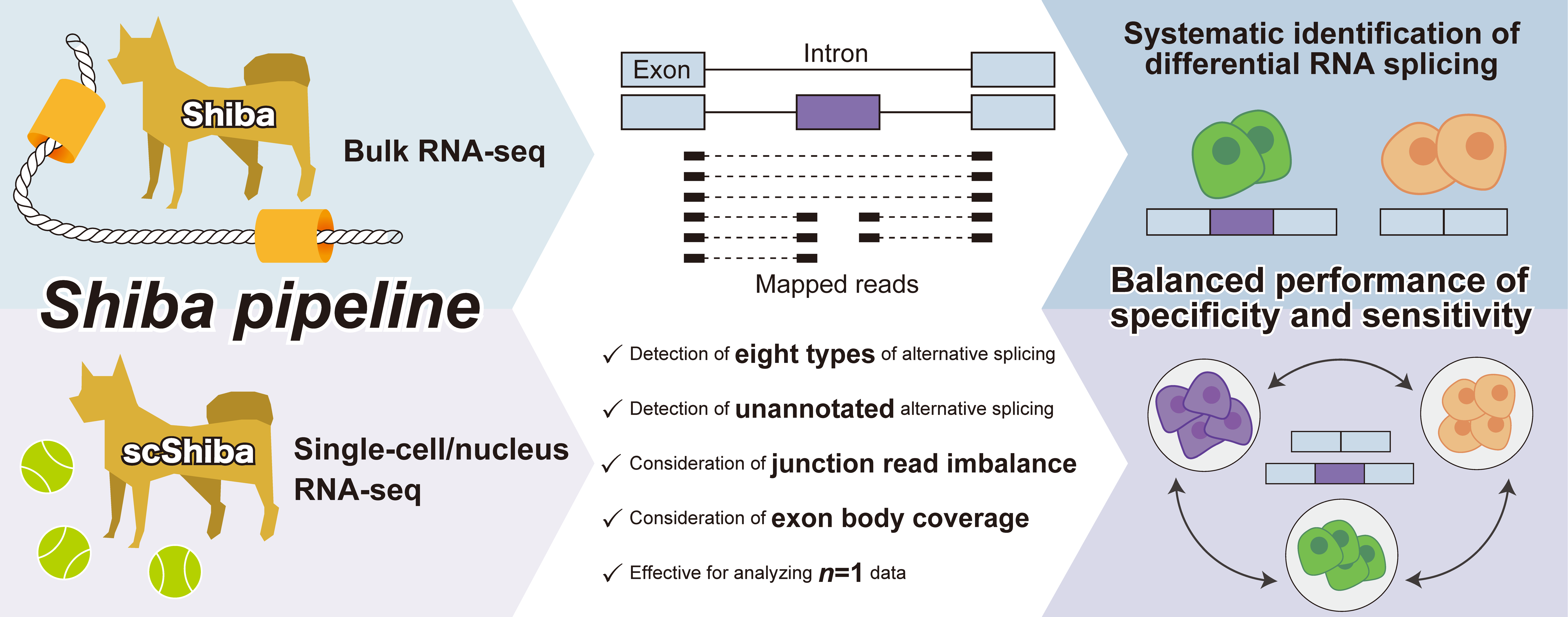
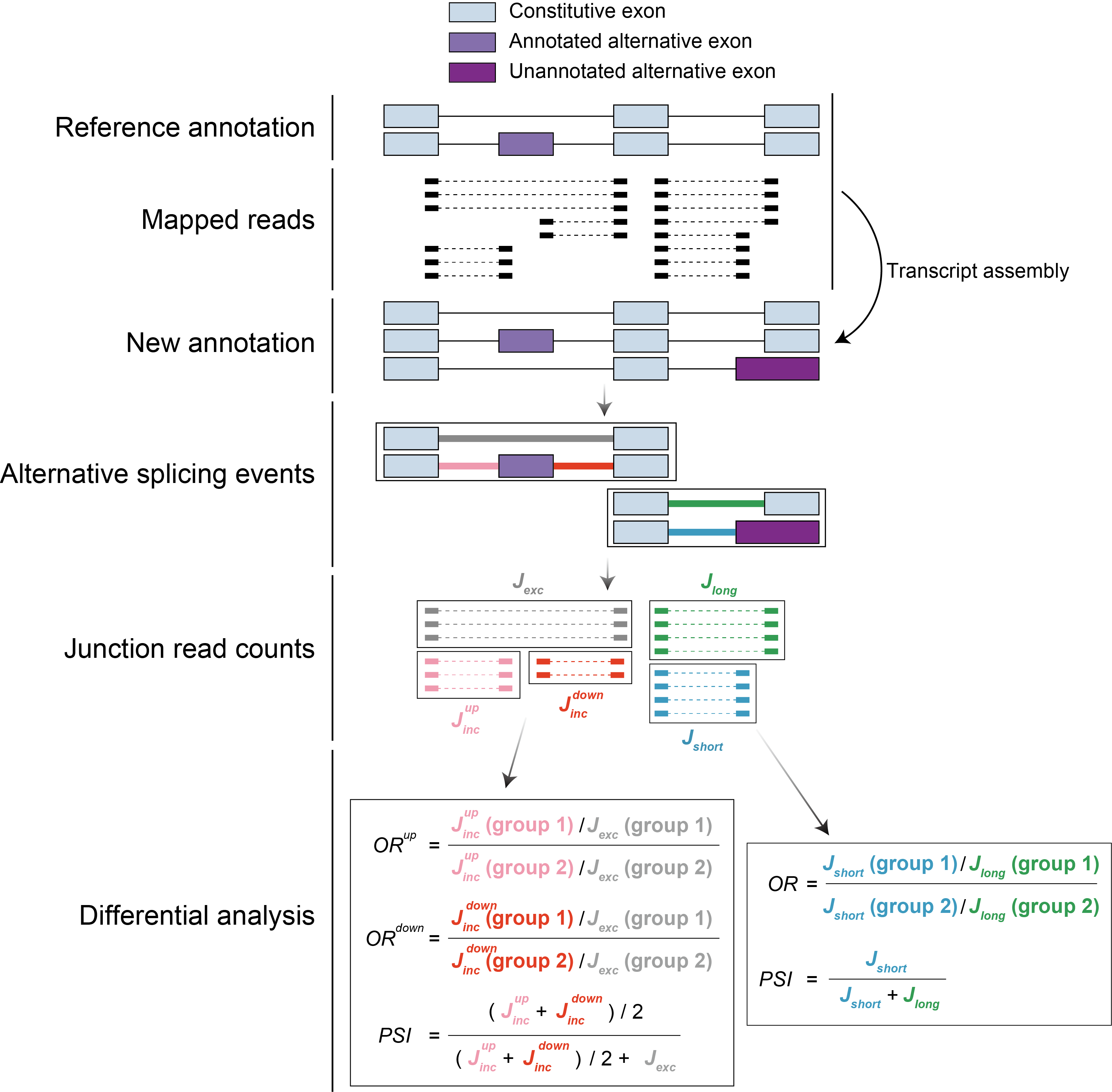 Kubota et al, Nucleic Acids Research 53(4), 2025, gkaf098.
Kubota et al, Nucleic Acids Research 53(4), 2025, gkaf098.
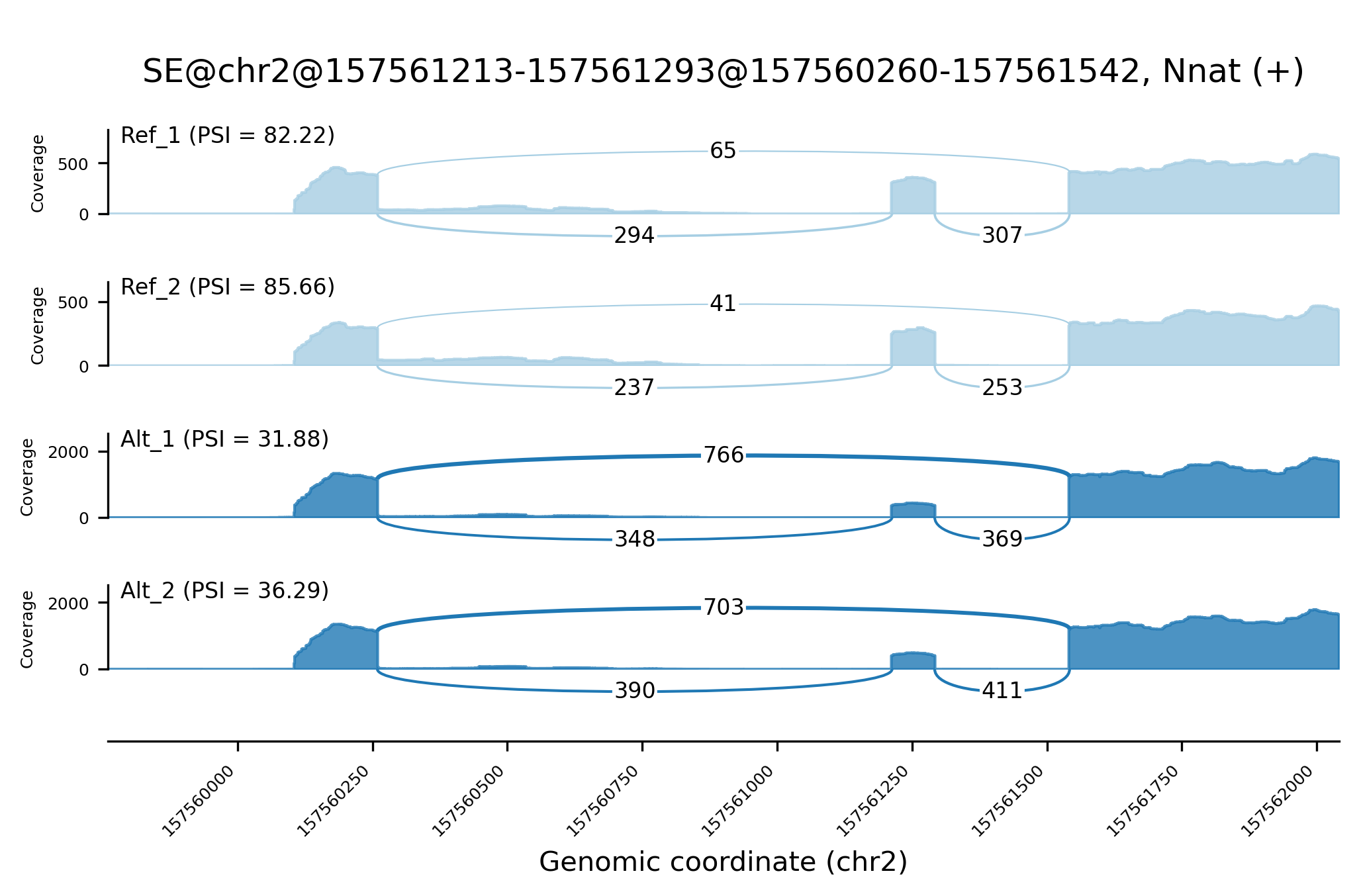
Alternative RNA splicing events identified in Shiba can be visualized by shiba2sashimi, a utility to create Sashimi plots.
Mapping of functional genomic variants in human disease risk
It has been largely unknown which and how genomic variants affect gene expression level and human disease risk. Previously I have worked on developing computational methods for identifying functional variants in the human genome.
Mapping of promoter usage QTL
I developed a computational method that enables mapping of genomic variants associated with promoter activity, called promoter usage QTL (puQTL).
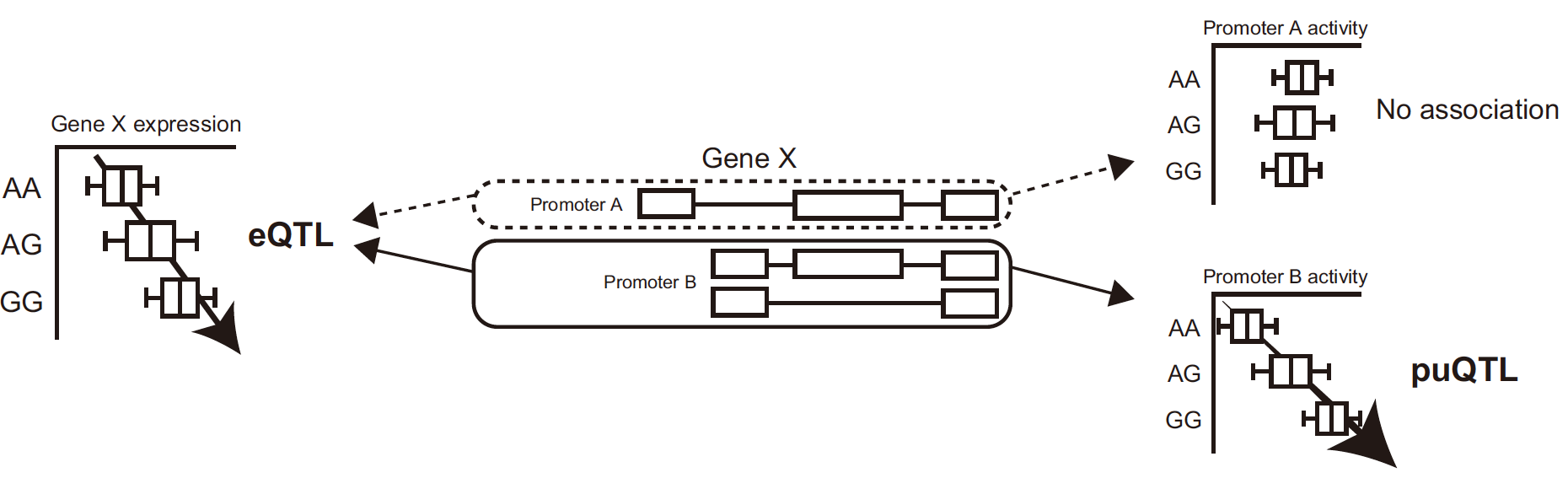
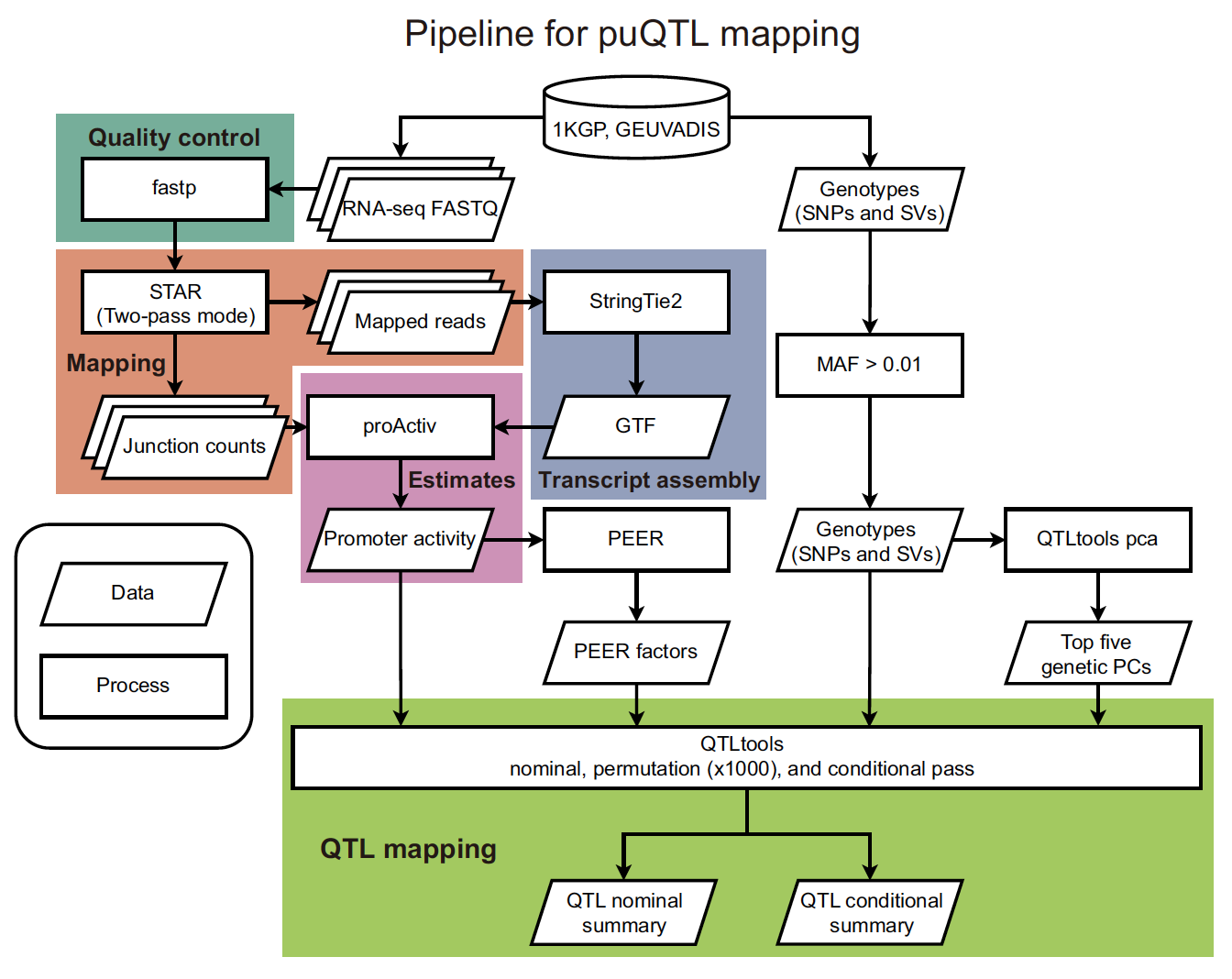 Kubota and Suyama, PLoS Comput. Biol. 18(8): e1010436. 2022.
Kubota and Suyama, PLoS Comput. Biol. 18(8): e1010436. 2022.
Functional variants in TF footprints and immune disease risk
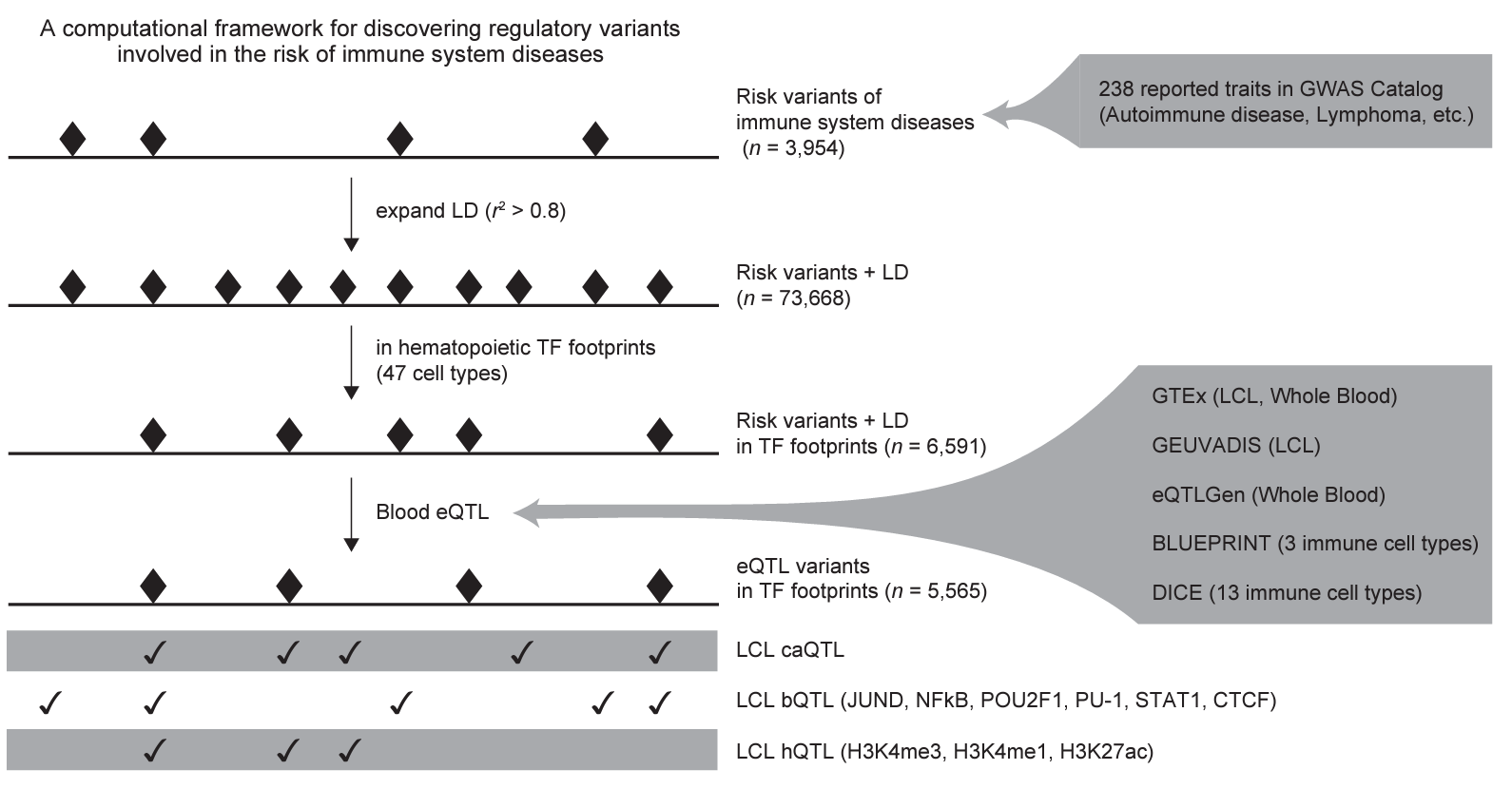 Kubota and Suyama, bioRxiv 2021.03.22.436360
Kubota and Suyama, bioRxiv 2021.03.22.436360
A genome-wide survey of functional variants associated with psoriasis risk
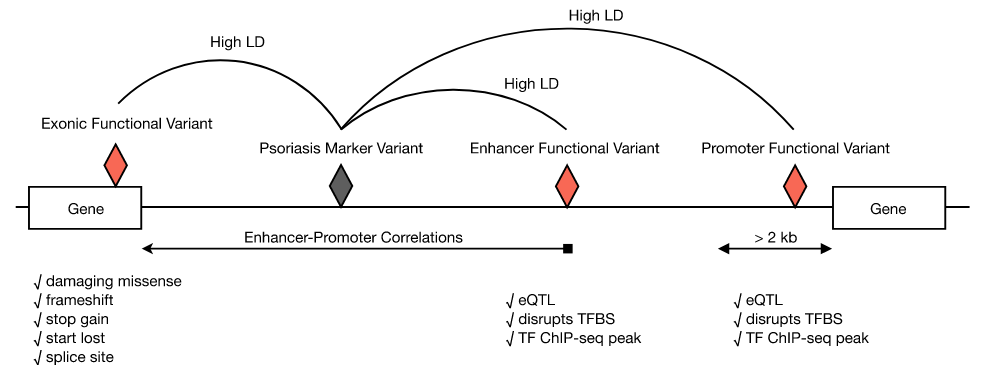 Kubota and Suyama, BMC Med. Genomics 13, 8, 2020.
Kubota and Suyama, BMC Med. Genomics 13, 8, 2020.
